Edge computing has been of great importance to gamers and streamers relying on quick and responsive connections. With the constantly increasing complexity and popularity of online games and live streaming platforms, the slightest performance and experience can be influenced by slight delays.
Conventional models of data processing are frequently based on remote data centers, which may add latency that is perceptible when using them in competitive play or real time content generation. The concept of edge computing alters this situation since processing moves nearer to the user, eliminating delays and enhancing the overall digital experiences.
Understanding Edge Computing
The concept of processing data near its source is known as edge computing as opposed to transmitting data over a long distance to centralized servers. To gamers and streamers, it implies that activities like player movements and voice chat, or even stream encoding can be processed by local servers. Through reducing the physical distance that the data has to cover, edge computing reduces the duration required by information to transfer between the user and the service.
This strategy is contrary to conventional cloud computing where data is usually transported over hundreds and even thousands of miles before it is processed. Cloud systems are powerful but distance presents inescapable delays. Edge computing is used in a complement to cloud infrastructure, where time-sensitive processors are performed by the local infrastructure and less urgent processing is provided by central servers. The balance enables online platforms to provide quicker responses with no compromise on scalability or reliability.
Latency Reduction in Gaming
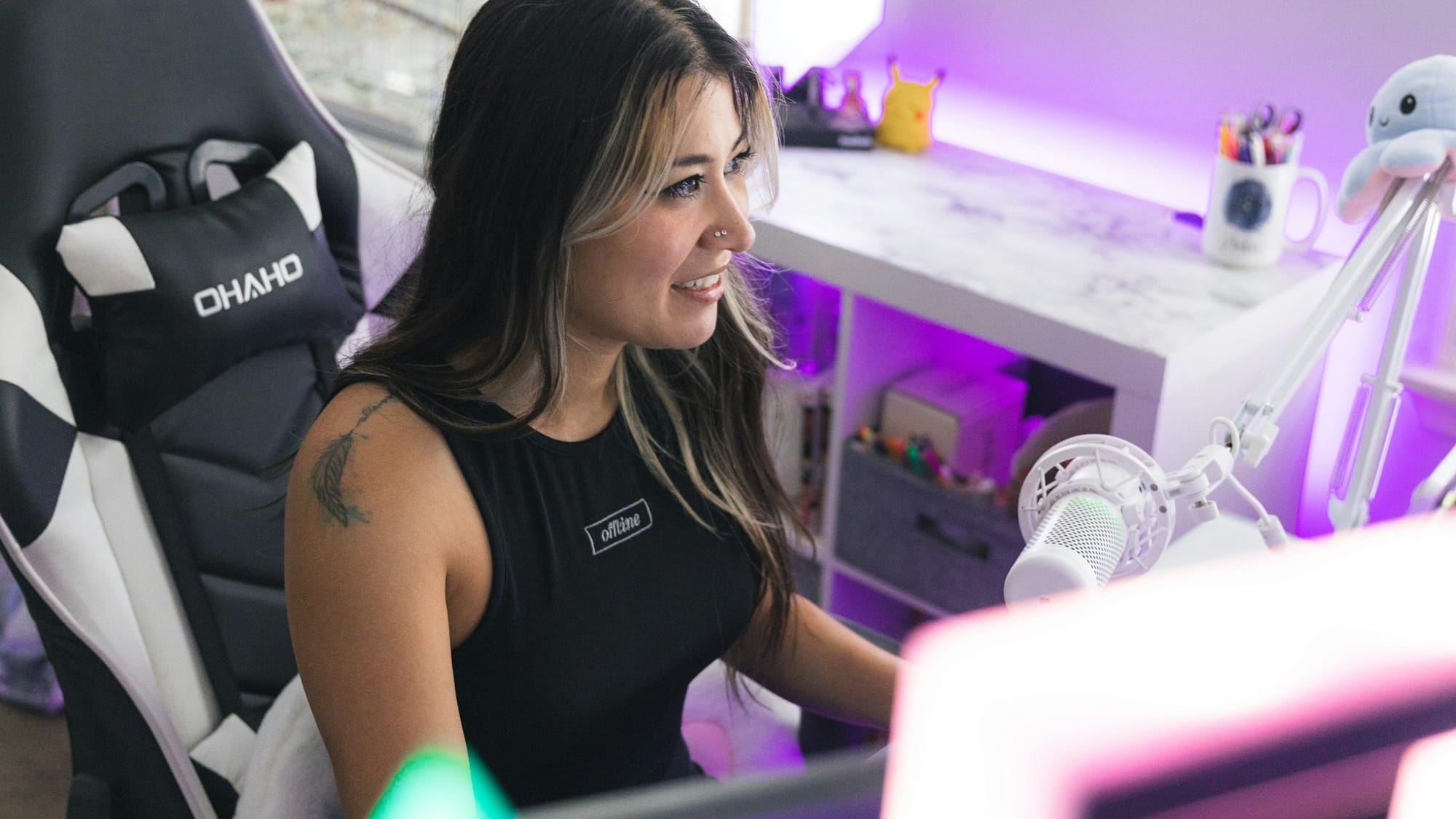
Gaming requires low latency, particularly in a competitive and multiplayer game. Even a delay of a few milliseconds may be the difference between the victory and defeat. By making game servers geographically nearer to players, edge computing can minimise latency, where inputs like clicking the mouse or controlling actions can be processed almost instantly.
This can be particularly noticeable to those players who are using home internet connections. Rather than moving data packets through the congested networks to access remote servers, they will be sent to the edge nodes nearby. This minimizes the lag, enhances coordination among players and a smoother overall experience is made possible. Since the edge based architectures are being embraced by increasingly more game developers, it is increasingly becoming possible to offer consistent low latency performance to more people.
Benefits for Live Streaming
Streamers also encounter another but similarly challenging problem of latency. Live streaming involves the encoding of video, transmitting the video to a platform, and sending it to the viewers in real time. Edge computing assists in doing part of this computation nearer to the streamer and reduces the latency between what occurs on screen and what the viewers observe.
Reduced latency is of great significance to interactive streams where interaction with the audience is a concern. Live chat response, polls, and real time reactions are also features that are also more natural when there are minimal delays. Through edge infrastructure, streaming platforms are able to offer creators more consistent performance even in the event of a high traffic event or peak usage.
Role of Network Infrastructure
Edge computing is very reliant on the network infrastructure. Internet providers are also instrumental in the implementation of edge nodes in regional networks, enabling the user to experience lower latency without having to alter their hardware. Such deployments take investments and coordination but can dramatically enhance the quality of the service in latency sensitive applications.
With the ongoing increase in the demand of gaming and streaming, the internet providers are more than willing to endorse edge computing solutions. Placing the processing resources near residential and urban centers will enable them to deliver more competitive services and achieve the customer expectations regarding speed and responsiveness. This change in infrastructure is a long term enhancement and not a short term optimization.
Impact on User Experience
As a user, the benefits of edge computing can be seen more as small but significant enhancements. Games become more interactive and streams load quicker and there is less lag in interactions. Such advantages add to a feeling of trustworthiness that increases confidence in the online services and platforms.
To both gamers and streamers, edge computing will help in providing a more engaging and interactive online environment. With the advancement of technologies and their usage, lower latency will supersede high-quality features instead of being considered a luxury. The change is useful in ensuring that online entertainment keeps growing without impacting on performance, and edge computing is a cornerstone of the modern internet experience.