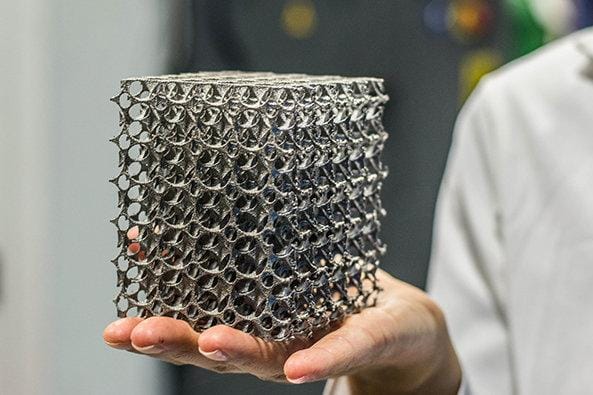
Imagine standing in a humming factory where metal powder dances under a laser’s gaze, layer by layer transforming into a jet engine part more complex than anything cast or forged before. Now imagine that same factory buzzing with algorithms—learning, predicting, optimizing in real time—turning yesterday’s static blueprints into living, learning, self-perfecting processes. This is not a vision of tomorrow; it’s the bold reality taking shape in workshops and design labs today.
At the heart of this shift is AI manufacturing—the convergence of data, algorithms, and 3D printing that’s redefining what’s possible. As industries from aerospace to healthcare double down on sustainability, customization, and speed, the pairing of artificial intelligence with additive manufacturing is proving to be the power couple reshaping production as we know it. But if we’re honest, most of us still carry outdated assumptions about what “printing parts with robots” can truly achieve. It’s time to challenge that.
Thinking Additive Manufacturing is Just Fancy Printing
For decades, the mental image of 3D printing was niche and static—a handy tool for prototyping or hobbyist tinkering, not serious industrial production. Many still see it that way: an experimental playground for designers to whip up parts on demand, but too slow, too unpredictable, too expensive for the grit and grind of real manufacturing lines.
Yet this mental trap misses the real story. The true revolution isn’t just the printer; it’s the intelligence driving it. In traditional workflows, once a design is finalized, it’s etched in digital stone. Any tweaks demand costly restarts, human guesswork, and time-consuming iterations. But the demands of modern industry—lighter parts, lower costs, smaller carbon footprints—don’t care about yesterday’s bottlenecks.
Today, manufacturers tapping into additive manufacturing aren’t just layering metal powders. They’re layering insights. Data flows through every stage, from simulation and design to in-situ monitoring and post-production quality control. Machines armed with AI algorithms can learn from every print cycle, spot defects before they happen, and even tweak designs on the fly. This dynamic loop replaces static plans with living feedback systems.
Consider how industries using advanced 3D printing for aerospace parts now rely on AI-driven predictive models. Instead of only catching errors after a batch is ruined, these systems monitor the entire build layer by layer, flagging anomalies instantly. The result? Higher yield rates, faster certifications, and an unprecedented ability to scale production without scaling defects. In short, the days of “print and pray” are over. But only if we unlearn the myth that 3D printing alone is enough.
Machines that Learn, Parts that Improve
So what does this new lens reveal? It shows us that AI manufacturing is not just a tool—it’s a co-pilot. One that learns, reasons, and refines designs far beyond what human engineers could juggle alone. At the design stage, generative AI software takes a simple input—a weight limit here, a stress constraint there—and spins out thousands of optimized shapes in seconds. These aren’t just theoretical models; they’re practical, testable forms ready for printing.
In quality control, AI’s role expands even further. Advanced image recognition and sensor analytics now catch deviations invisible to the naked eye. A thermal spike, a micro-void, a subtle warp—AI sees them all in real time. Some companies are even experimenting with closed-loop systems where AI not only detects flaws but immediately recalibrates printing parameters to correct them mid-build. That means fewer scrapped parts, tighter tolerances, and production lines that learn from each print.
And it doesn’t stop there. Once parts are deployed—inside engines, implants, or industrial machines—IoT sensors can feed performance data back into the design loop. This turns additive manufacturing into a living process: parts evolve, materials improve, production methods self-optimize. This shift is why advanced manufacturers increasingly embed AI solutions not as a bolt-on but as the backbone of their digital factories. The frontier is not just smarter machines, but entire systems that learn at scale.
Beyond the Obvious: The Invisible Hand of AI
Here’s the twist: many of the biggest gains from AI manufacturing don’t come from flashy design or futuristic robotics—they come from hidden efficiencies. Scheduling, supply chain optimization, maintenance prediction—these back-end improvements quietly slash costs, reduce waste, and free up engineers to tackle new challenges.
What’s emerging is an ecosystem where human creativity and machine learning co-create. AI handles the grunt work of permutations and anomaly detection; engineers do what they do best: imagine the impossible. This is the true promise of advanced additive manufacturing: not just making things differently, but thinking differently about what we make—and how we make it better, faster, and cleaner.
Conclusion: A New Lens for the Future
If the past decade taught us anything, it’s that standing still in manufacturing means falling behind. AI manufacturing asks us to step into a world where data, design, and production are no longer silos but symbiotic. The lesson? Innovation doesn’t come from a bigger machine—it comes from a smarter one.
The next time you hear “additive manufacturing,” think beyond the printer nozzle. Think of the learning loops, the algorithms sifting mountains of data, the parts that tell their own story. Then ask: what possibilities could I unlock if I treated every design as a living experiment? The factories of the future are already listening. Are you ready to learn alongside them?