If you've ever tried to play a video on Linux without having any media player installed, you'd know the familiar "cannot open the file" error or something of the sort. While other operating systems like Windows come with basic media players, many Linux distros don't come with a player to handle the enormous variety of video and audio formats out there.
Fortunately, you can always install your preferred heavyweight media player like VLC to handle your media files. I use VLC because it's free, open-source, and can play almost any media format in existence.
Getting VLC up and running on your Linux distribution is a straightforward process. This guide will show you how to install VLC on Ubuntu Linux for a perfect media playback experience.

How to Install VLC Player on Linux
Step 1: Update Your System
Before installing anything new, it’s always a good idea to refresh your package list to make sure you’re getting the latest versions. On your terminal, run:
sudo apt update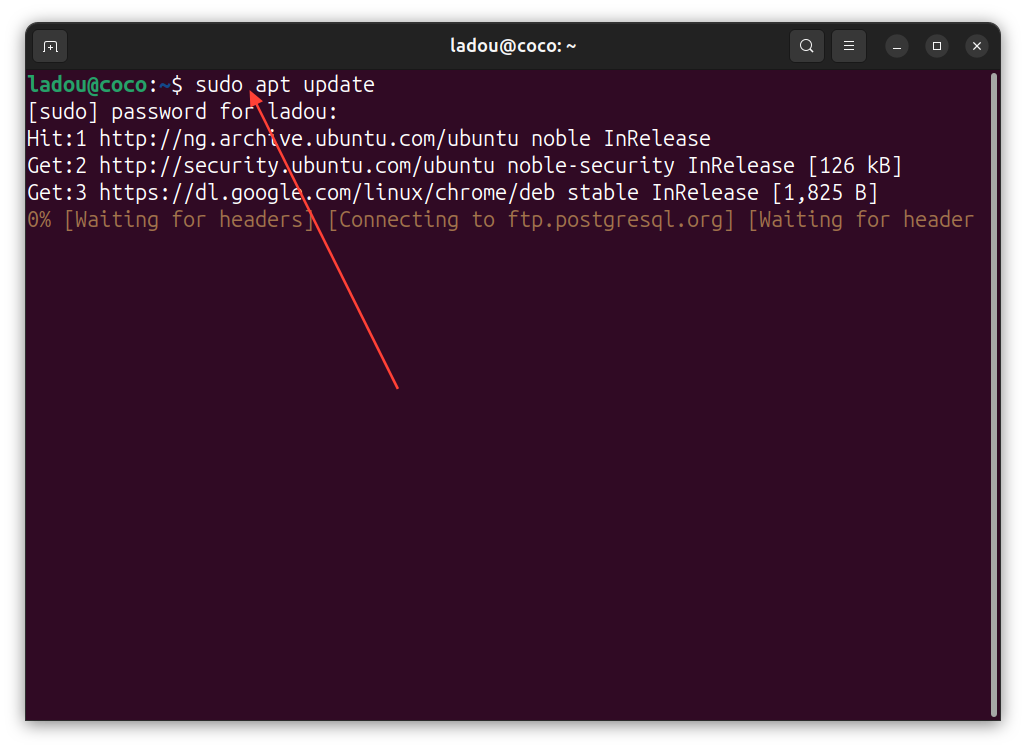
Step 2: Upgrade Installed Packages
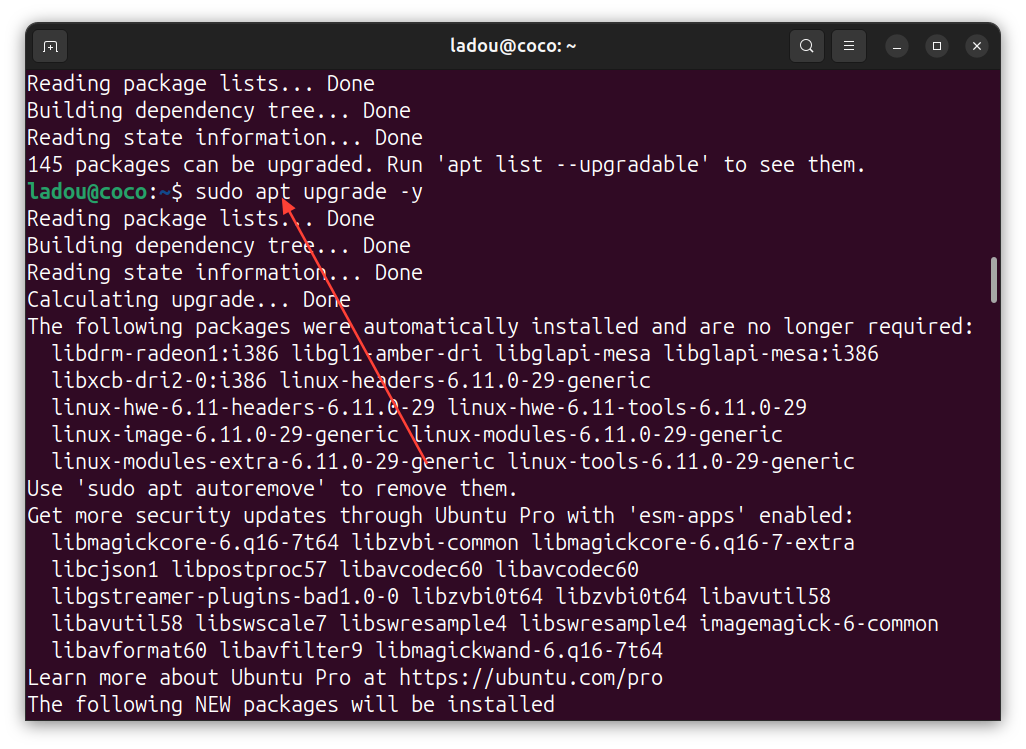
Next, let’s upgrade any existing packages to avoid conflicts:
sudo apt upgrade -yThe “-y” flag automatically confirms the upgrade; no extra prompts needed.
- Alternatively, you can run steps one and two in one line like this:
sudo apt update && sudo apt upgrade -yThis will also fetch your latest packages from Ubuntu’s repositories and make the upgrade for you.
Step 3: Install VLC.
Using the apt package manager, install VLC like this:
sudo apt install vlc -y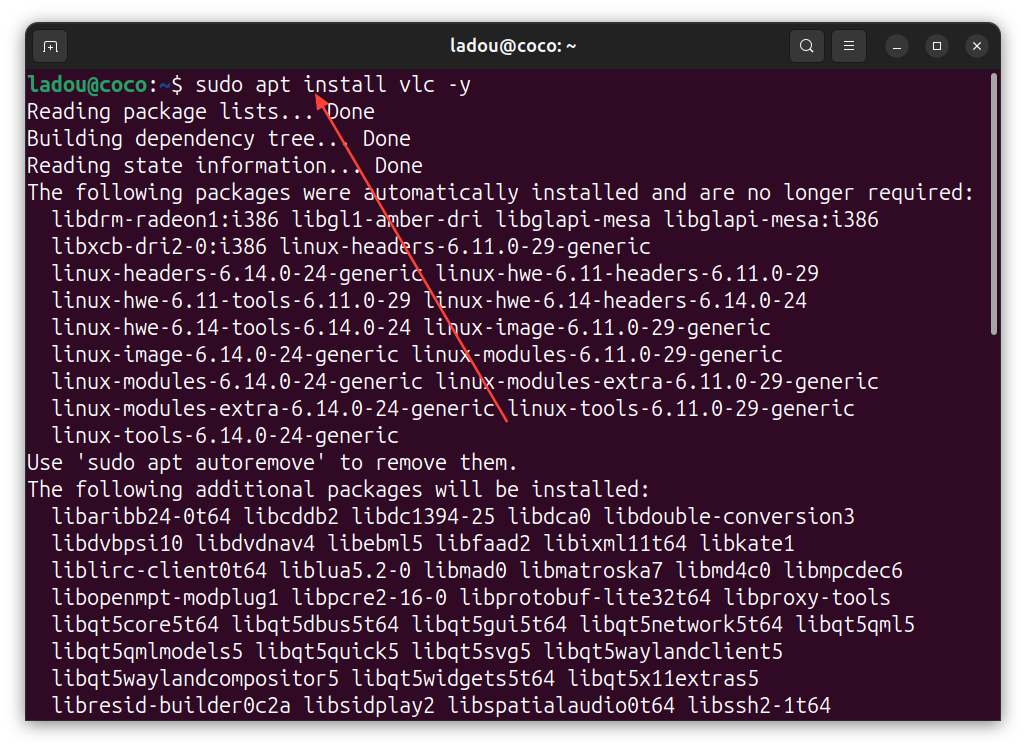
Step 4: Launch VLC.
You can now launch VLC either from the terminal or through the Ubuntu application menu.
How to uninstall VLC Player on Linux
Step 1: Remove the VLC player
- Remove the VLC player package by running the command below:
sudo apt remove vlc -y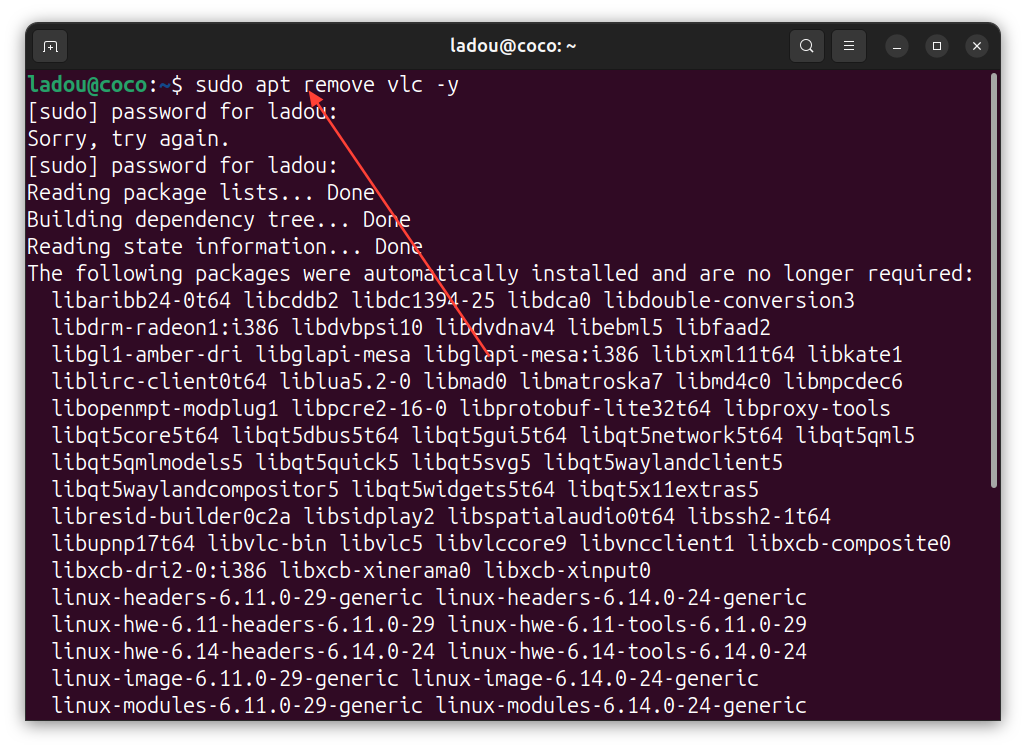
Step 2: Remove the VLC config file
- The previous command removed just the package, but the configuration files are still there. To remove the config files, run the command below:
sudo apt autoremove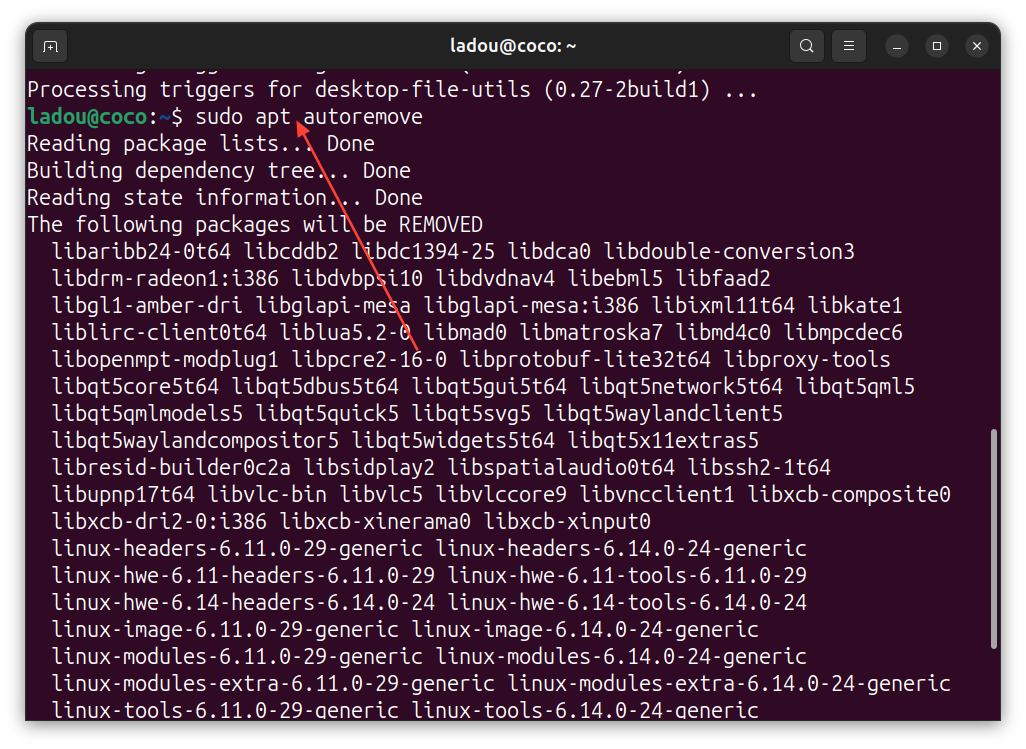
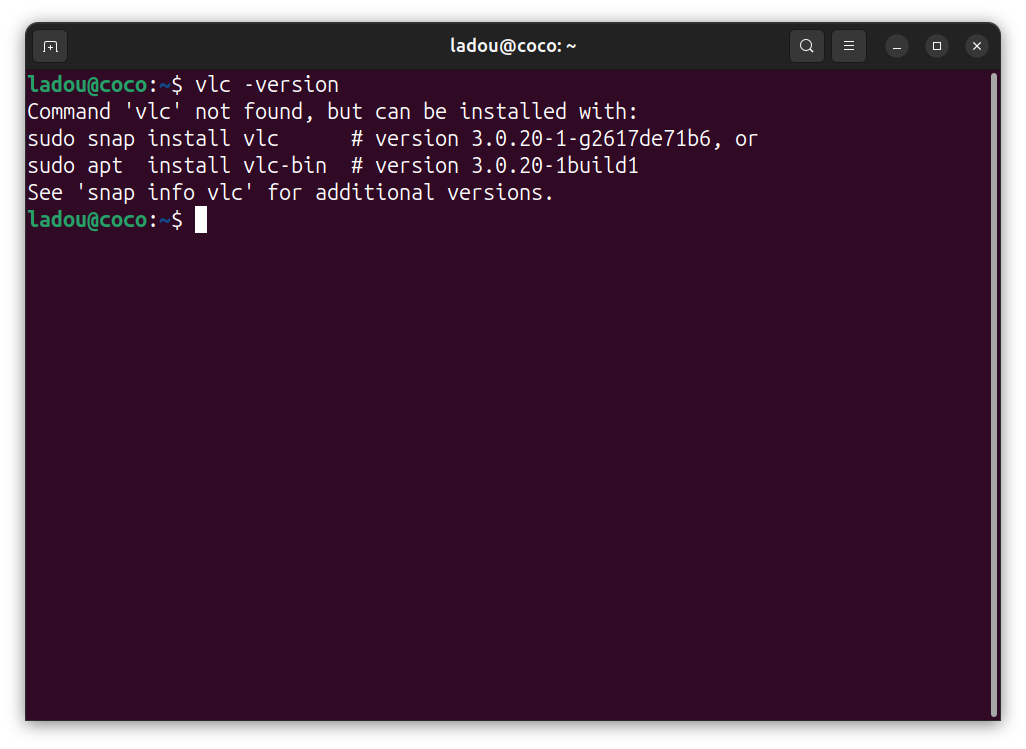
- If you go to your application menu or check from the terminal, you'll see it's no longer in your system.
Conclusion
The fact that VLC can handle virtually any media format easily makes it an ideal media tool on any Linux system, effectively putting an end to file compatibility issues once and for all.
Aside the basic movie watching, you can go to its settings to explore more advanced features like creating playlists, adjusting advanced video filters, or even using it to stream content. It's one of those rare applications that is both simple enough for beginners and powerful enough for pros.
Image Credit: Oyinebiladou Omemu/techloy.com